SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization. SEO is the practice of optimizing your website and its content to improve its visibility and ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs).
The goal of SEO is to increase the organic (non-paid) traffic to your website by making it more attractive and relevant to search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo.
Search engines use complex algorithms to determine the order in which websites appear in search results.
SEO involves various techniques and strategies to align your website with these algorithms, ultimately helping your site rank higher for relevant search queries.
The higher your website ranks, the more likely it is to be clicked on by users searching for related information or products.
Here’s a quick overview of everything we’re going to cover:
- What is SEO?
- Types of SEO
- Importance of SEO
- How do Search Engines work?
- How does SEO work?
- How to develop your SEO skills?
Types of SEO
There are three main types of SEO: On-Page SEO, Off-Page SEO, and Technical SEO. Let’s break down each type:
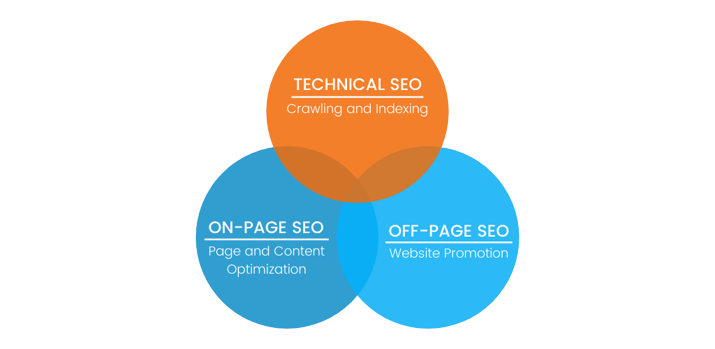
- On-Page SEO: On-page SEO focuses on optimizing individual web pages to improve their visibility in search engine results. It involves making changes directly to your website’s content and structure. Key elements of on-page SEO include:
- Quality Content: Creating valuable, informative, and engaging content that addresses users’ needs and questions.
- Keyword Optimization: Incorporating relevant keywords naturally into page titles, headings, and content.
- URL Structure: Creating user-friendly and descriptive URLs that reflect the content of the page.
- Image Optimization: Using descriptive alt text for images to improve accessibility and search visibility.
- Meta Tags: Optimizing meta titles and descriptions to accurately describe the content and attract clicks.
- Internal Linking: Connecting pages within your website to guide users and distribute link authority.
- User Experience: Ensuring your website is easy to navigate, mobile-friendly, and loads quickly.
2. Off-Page SEO: Off-page SEO involves actions taken outside of your website to improve its authority and reputation in the eyes of search engines. It’s mainly about building high-quality backlinks and creating a positive online presence. Key aspects of off-page SEO include:
- Social Signals: Engaging on social media platforms to boost your website’s visibility and online influence.
- Backlink Building: Acquiring links from reputable and relevant websites to demonstrate your website’s credibility.
- Influencer Outreach: Collaborating with influencers to promote your content and expand your reach.
- Online Mentions: Encouraging mentions and references of your brand across the internet to enhance recognition.
- Guest Blogging: Writing articles for other authoritative websites to showcase your expertise and gain exposure.
3. Technical SEO: Technical SEO focuses on the technical aspects of your website that impact its search engine performance. It’s about ensuring that search engines can properly access, crawl, and understand your website’s content. Key components of technical SEO include:
- Crawlability: Ensuring search engines can easily navigate and index your website’s pages.
- Structured Data: Implementing structured data markup to help search engines understand your content better.
- Page Speed: Optimizing page loading times for a better user experience and search ranking.
- Sitemaps: Creating XML sitemaps to guide search engines in discovering and indexing your pages.
- Mobile-Friendliness: Ensuring your website works well on mobile devices, is crucial for modern search algorithms.
- Canonicalization: Managing duplicate content issues to prevent confusion for search engines.
Importance of SEO

SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is important for several reasons, as it plays a crucial role in enhancing the online presence and visibility of websites. Let’s delve into the details of why SEO matters –
- Increased Organic Traffic – Organic traffic refers to the visitors who find your website through unpaid search results. SEO helps improve your website’s ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs), which in turn increases the likelihood of users clicking on your website. A higher ranking means more visibility and more visibility leads to more organic traffic.
- Better User Experience – SEO involves optimizing various aspects of your website, such as site structure, page speed, and mobile-friendliness. These improvements enhance the user experience, making it easier for visitors to navigate your site and find the information they’re looking for. A positive user experience leads to longer visit durations and lower bounce rates, which can indirectly impact your SEO.
- Cost-Effectiveness – Organic search results are free, unlike paid advertising where you pay for each click. While SEO does require an investment of time and effort, the long-term benefits often outweigh the costs, making it a cost-effective strategy for sustainable online visibility.
- Credibility and Trust – Websites that appear at the top of search results are often seen as more credible and trustworthy by users. Effective SEO not only helps your website rank higher but also reinforces your brand’s authority and reputation within your industry.
- Higher Conversion Rates – When your website is optimized for relevant keywords and provides valuable content, it attracts visitors who are genuinely interested in your products or services. These targeted visitors are more likely to convert into customers, subscribers, or leads, thereby increasing your conversion rates.
- Long-Term Results – Unlike some other digital marketing tactics that provide immediate but short-lived results, SEO is a long-term strategy. Once your website starts ranking well, it can maintain its position for a considerable time even with minor ongoing efforts.
- Competitive Advantage – In today’s digital landscape, most businesses have an online presence. Effective SEO allows you to stand out from the competition and capture a larger share of the online market.
- Local and Mobile Search Optimization – With the rise of mobile devices, local search optimization has become crucial. Local SEO techniques help brick-and-mortar businesses reach customers in their vicinity. Mobile users often search for information on the go, and a well-optimized mobile-friendly website is more likely to capture their attention.
- Adapting to Search Engine Algorithms – Search engines continually update their algorithms to deliver the most relevant and high-quality results to users. Staying up-to-date with these changes and adapting your SEO strategies accordingly ensures that your website remains visible and relevant in search results.
- Analytics and Insights – SEO tools provide valuable data and insights about your website’s performance, user behavior, and keyword trends. This data can help you refine your marketing strategies and make informed business decisions.
How do search engines work?
Search engines work by indexing and retrieving information from the vast amount of data available on the internet. The process can be broken down into several key steps-
- Crawling – Search engines use automated programs called “crawlers” or “spiders” to systematically browse the web. These crawlers follow links from one page to another, visiting websites and collecting information about their content. As they visit pages, they store data about the page’s URL, content, keywords, and other relevant information.
- Search Query Processing – When a user submits a search query, the search engine processes the query to understand its intent and the keywords involved. The query is then matched against the indexed content using the ranking algorithm to identify the most relevant results.
- Indexing – Once the crawlers collect data from web pages, the information is organized and stored in a massive database called an index. The index is like a catalog that contains information about the words, phrases, and other elements present on each webpage. This process involves breaking down the content into smaller parts for easier retrieval.
- Retrieval and Display – After ranking the results, the search engine presents them to the user in a list format on the search engine results page (SERP). The results are usually displayed with a title, brief description (snippet), and URL. The user can click on the search results to access the full webpage.
- Ranking Algorithm – When a user enters a search query, the search engine’s ranking algorithm comes into play. This algorithm sifts through the indexed data to find pages that are most relevant to the query. The ranking algorithm takes various factors into account, including keyword relevance, user engagement, page quality, backlinks, and more.
- Continuous Update – The internet is dynamic, with new content being added and existing content changing frequently. Search engines continually update their indexes by recrawling websites to ensure they have the latest information. This process allows search engines to provide up-to-date search results.
How does SEO work?
SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is the practice of optimizing a website or online content to improve its visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs). The goal of SEO is to increase organic (non-paid) traffic to a website by making it more relevant and authoritative in the eyes of search engines. Here’s how SEO works-
- Keyword Research – SEO begins with identifying the keywords and phrases that are relevant to your content and that people might use when searching for information related to your topic. These keywords form the basis of your optimization efforts.
- High-Quality Content – Content is a critical component of SEO. It should be valuable, informative, and relevant to the user’s search intent. High-quality content has a better chance of ranking well in search results and attracting backlinks.
- On-Page Optimization – This involves optimizing the content and HTML source code of your web pages. Key elements to optimize include –
- Title Tags: These are HTML tags that define the title of a web page. They should be descriptive and contain relevant keywords.
2. Meta Descriptions: Brief summaries that appear in search results. They should be compelling and include keywords.
3. Header Tags: These HTML tags (H1, H2, etc.) indicate the structure of your content. They should be used to organize content and include keywords.
4. Keyword Usage: Incorporate your target keywords naturally throughout your content, including in headings, paragraphs, and image alt text.
5. URL Structure: Create URLs that are descriptive and include keywords if possible.
- Page Speed – Faster-loading websites provide a better user experience, and search engines consider this when ranking pages. Compress images, use browser caching, and optimize code to improve page speed.
- Mobile-Friendliness – With the increasing use of mobile devices, search engines prioritize mobile-friendly websites. Ensuring your site is responsive and loads quickly on mobile devices is important for SEO.
- Technical SEO –This involves optimizing the technical aspects of your website to make it easier for search engines to crawl and index your content. This includes:
- User Experience (UX) – Positive user experiences, including low bounce rates and longer on-page time, signal to search engines that your content is valuable and relevant.
- Sitemap: A file that lists all the pages on your site, helping search engines understand its structure.
- Robots.txt: A file that provides instructions to search engine bots about which pages to crawl and index.
- Canonical Tags: Used to indicate the preferred version of a page when duplicate content exists.
- Schema Markup: Code that helps search engines understand the context of your content, improving the chances of rich snippets appearing in search results.
- Regular Updates – Keeping your content up-to-date and relevant demonstrates your website’s ongoing authority and expertise on the subject.
- Backlinks – Search engines consider the number and quality of links pointing to your website as a measure of its authority and relevance. Building high-quality backlinks from reputable sources is an important aspect of SEO.
- Monitoring and Analysis – Regularly track your website’s performance using tools like Google Analytics and Search Console. Analyze which strategies are working and which areas need improvement.
How to develop your SEO skills?
- Advanced Learning:
- Dive deeper into advanced topics such as technical SEO, structured data, and advanced link-building strategies.
- Study algorithm updates (e.g., Google’s Core Updates) and understand their implications on search rankings.
2. Master Analytics:
- Gain a deep understanding of Google Analytics and Google Search Console.
- Learn to interpret data and draw insights to make informed SEO decisions.
3. Content Strategy:
- Develop a comprehensive content strategy that aligns with SEO goals.
- Learn to create content that serves user intent and ranks well in search results.
4. Mobile and Voice Search:
- Deepen your knowledge of mobile-friendly design and voice search optimization.
- Optimize for voice search queries and mobile-first indexing.
5. Technical Proficiency:
- Focus on technical SEO aspects like site speed optimization, mobile optimization, and site structure.
- Learn to identify and fix technical issues that might affect your website’s performance.
6. Schema Markup and Rich Snippets:
- Learn to implement schema markup to enhance search results appearance (rich snippets).
- Understand different types of schema markup and their impact on SEO.
7. Local and International SEO:
- Master local SEO techniques for businesses targeting specific geographic areas.
- Understand the nuances of international SEO when targeting multiple countries or languages.
8. Algorithm Updates and Penalties:
- Stay informed about Google algorithm updates and their effects on search rankings.
- Learn how to recover from penalties (e.g., manual actions) if your site is impacted.
9. Mobile and Voice Search:
- Deepen your knowledge of mobile-friendly design and voice search optimization.
- Optimize for voice search queries and mobile-first indexing.
10. Advanced Tools:
- Explore advanced features of SEO tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Screaming Frog.
- Learn to use these tools for in-depth analysis and reporting.
